Figure 1: (Left) The 3-dimensional dark matter map of
the Universe inferred from one of the six HSC observation areas is shown
in the background with various shades of blue (brighter areas have more
dark matter). The map was inferred from the distortions of shapes of
galaxies in the HSC data which are indicated by white sticks. The stick
lengths represent the amount of distortion and the angle of the stick
corresponds to the direction of the distortion. (Right) The measurements
are enabled by the light from distant galaxies that travels through the
Universe and gets deflected by matter at different epochs in the
Universe, before reaching the Subaru Telescope.(Credit: HSC
Project/UTokyo)
Using the Subaru Telescope, the Hyper Suprime-Cam (HSC) survey
collaboration team has made and analyzed the deepest wide field map of
the three-dimensional distribution of matter in the Universe. Led by
Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (Kavli
IPMU) Project Assistant Professor Chiaki Hikage, a team of scientists
primarily from Japan including National Astronomical Observatory of
Japan (NAOJ), Taiwan and Princeton University has used the gravitational
distortion of images of about 10 million galaxies to make a precise
measurement of the lumpiness of matter in the Universe. By combining
this measurement with the European Space Agency Planck satellite's
observations of the cosmic microwave background, and other cosmological
experiments, the team has been able to further constrain the properties
of the "dark energy" that dominates the energy density of the Universe.
Although dark matter cannot be directly seen, its gravitational
effects, predicted by Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity,
cause stretching and squeezing of the light from distant galaxies as
they travel across the cosmos, to be detected by the Subaru Telescope.
They are witness to the growth of cosmic structure (Figure 1,
left) and can be used to unlock the mysteries of dark energy. The
simplest model for dark energy was introduced by Einstein, termed the
"Cosmological Constant." This model can explain all existing
observations, including those of HSC.
The gravitational lensing effect from the distribution of dark matter
in the Universe is quite weak, but results in small but measurable
distortions in the images of the galaxies in the HSC images. Like a
pointillist painting, the distorted images of millions of galaxies
located at a range of distances paint a three-dimensional picture of the
distribution of matter in the Universe (Figure 1,
right). The HSC research team has precisely characterized the
fluctuations or lumpiness of the distribution of dark matter, and the
change in that lumpiness over billions of years - from its adolescence
to adulthood. This lumpiness is a key parameter that describes how
structure in the universe grew from its initial smooth beginnings after
the Big Bang to the galaxies, stars and planets we see today.
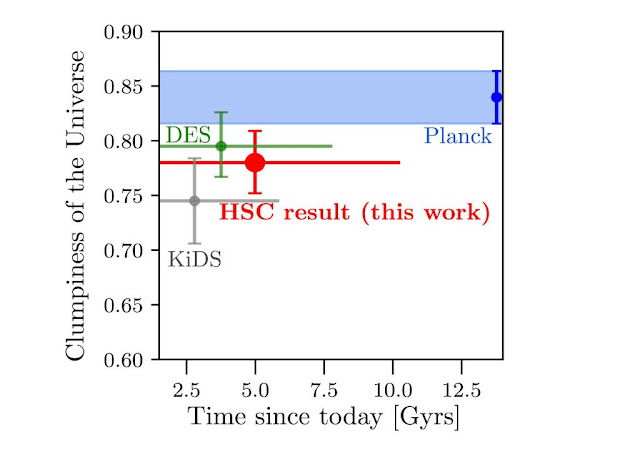
With the high-precision HSC data, the team measured the lumpiness with a precision of 3.6% (Figure 2),
which is similar to the precision with which it has been measured by
other lensing surveys. These other surveys, including the Dark Energy
Survey (DES) carried out on the Victor Blanco Telescope in Chile,
surveyed brighter and thus nearer-by galaxies than did the HSC; the
consistency of results at different distances and thus cosmic epochs
gives confidence in the robustness of the results.
Figure 2: The cosmological constraints on the clumpiness of the Universe today (S8)
predicted using observations at different times in the Universe. The
HSC measurement of the clumpiness of the Universe is shown with the red
symbol and are among the farthest measurements using weak gravitational
lensing. These should be compared with the Planck results obtained from
observations of the cosmic microwave background in the very early
Universe and other contemporary weak lensing experiments the Kilo Degree
Survey (KiDS) and DES. (Credit: HSC Project/UTokyo)
When compared to the fluctuations expected from those seen in the
Universe's infancy by the Planck satellite, the HSC measurements offer a
consistent picture of the cosmological model (Figure 3).
The Universe today is dominated by dark matter and dark energy, and
that dark energy behaves like Einstein's cosmological constant (Figure 4).
Figure 3: The cosmological constraints on the
fractional contribution of matter to the energy budget of the Universe
(rest of it corresponds to dark energy), and the clumpiness of the
matter distribution today (S8), as inferred from the analysis
of the 3d dark matter map. The results of the clumpiness of the matter
distribution from HSC observations of the distant Universe using weak
gravitational lensing are consistent with results from other similar
observations (DES and KiDS) of slightly nearby Universe. The results
from the cosmic microwave background observations during the Universe's
infancy obtained by the Planck satellite are shown in blue. (Credit: HSC
Project)
Figure 4: Cosmological constraints on the dark energy
equation of state (blue contours alone from HSC), red contours
corresponds to constraints after combining with cosmological results
from the Planck CMB satellite and other contemporary cosmological
measurements using Supernovae and Baryon acoustic oscillations. (Credit:
HSC Project)
However, taken together the results from weak lensing surveys prefer a
slightly smaller value of fluctuations than that predicted by the Planck
satellite (Figure 5).
This could just be a statistical fluctuation due to the limited amount
of data available, or might be a signature of the breakdown of the
standard model of the Universe, based on General Relativity and the
cosmological constant.
Figure 5: The weak lensing surveys such as HSC prefer a
slightly less clumpy Universe than that predicted by Planck. The
pictures show the slight but noticeable difference as expected from
large computer simulations. Is this difference a statistical
fluctuation? Astronomers all around the world continue to collect more
and more data to answer this question. (Credit: UTokyo, Image provided
by Kavli IPMU Project Assistant Professor Takahiro Nishimichi)
The HSC team conducted the HSC survey using the Subaru Telescope on
the summit of Maunakea, one of the best astronomical sites in the world.
The combination of a large primary mirror with a diameter of 8.2
meters, a wide field camera that can observe the area of 9 full moons in
a single shot, and superb image quality producing sharp images of each
galaxy, makes the telescope well suited to conduct a wide yet deep
imaging survey of the sky. The survey has covered about 140 square
degrees of sky (the area of 3000 full moons) over 90 nights.
The study required precise measurements of the shapes of galaxies.
Since the weak lensing effect is quite small, the HSC team had to
control various problems affecting the measurement of shapes, such as
distortions due to the atmosphere and the instrument itself. The team
overcame these difficulties by using detailed image simulations of the
HSC survey based on images from the Hubble Space Telescope.
When carrying out precise measurements of very small effects like
weak lensing, it is known that people have a tendency to decide that
their analysis is complete if their results confirm earlier results. The
HSC team performed a so-called blind analysis of their data in order to
avoid such 'confirmation bias." They carried out many tests of their
catalogs for more than a year without ever seeing the actual values of
cosmological parameters from their analysis or comparing with results
from other experiments, waiting until they were completely satisfied
with their results before allowing themselves to examine their
cosmological implications.
The HSC survey is on-going, the new HSC results come from a mere one
tenth of the final survey. Upon completion, the survey will put
considerably tighter constraints on cosmological parameters, deepening
our understanding and further testing our understanding of both dark
matter and dark energy.
HSC lead developer, Dr. Satoshi Miyazaki, from NAOJ's Advanced
Technology Center, commented on the new work based on the HSC data.
"This paper is a very important milestone of the HSC project where we
have peer reviews on the data analysis package to determine cosmological
parameters. At the same time, it also demonstrates the quality of the
HSC data compared with those of other projects. Scientifically, the
result is very exciting because it is consistent with what we have shown
in February 2018 suggesting that the number of dark matter halo is less
than the expectation based on a standard cosmological model."
The research paper is available as a preprint (Chiaki Hikage,
Masamune Oguri, Takashi Hamana, Surhud More, Rachel Mandelbaum, Masahiro
Takada, et al., "Cosmology from cosmic shear power spectra with Subaru Hyper Suprime-Cam first-year data") on arxiv.org,
and has now been submitted to the journal Publications of the
Astronomical Society of Japan and will undergo rigorous peer review by
the scientific community. This research is supported by KAKENHI
(JP15H03654, JP16K17684, JP16H01089, JP17H06599, JP18H04348, JP18K03693,
JP18H04350, JP15H05887, JP15H05892, JP15H05893, JP15K21733).
Links:
- Unprecedentedly Wide and Sharp Dark Matter Map (March 1, 2018 Subaru Telescope Press Release)
- Hyper Suprime-Cam Ushers in a New Era of Observational Astronomy (September 12, 2012 Subaru Telescope Press Release)
- Press release from Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe
Source: Subaru Telescope/Press Release