Massive stars end their lives in gigantic explosions, so-called
supernovae. Within millions of years of stable evolution, these stars
have built up a central core composed of mostly iron. When the core
reaches about 1.5 times the mass of the Sun, it collapses under the
influence of its own gravity and forms a neutron star. Enormous amounts
of energy are released in this catastrophic event, mostly by the
emission of neutrinos. These nearly massless elementary particles are
abundantly produced in the interior of the new-born neutron star, where
the density is higher than in atomic nuclei and the temperature can
reach 500 billion degrees Kelvin.
The physical processes that trigger and drive the explosion have been
an unsolved puzzle for more than 50 years. One of the theoretical
mechanisms proposed invokes the neutrinos, because they carry away more
than hundred times the energy needed for a typical supernova. As the
neutrinos leak out from the hot interior of the neutron star, a small
fraction of them is absorbed in the surrounding gas.
This heating causes
violent motions of the gas, similar to those in a pot of boiling water.
When the bubbling of the gas becomes sufficiently powerful, the
supernova explosion sets in as if the lid of the pot was blown off. The
outer layers of the dying star are then expelled into circumstellar
space, and with them all the chemical elements that the star has
assembled by nuclear burning during its life. But also new elements are
created in the hot ejecta of the explosion, among them radioactive
species such as titanium (44Ti with 22 protons and 22 neutrons) and
nickel (56Ni with 28 neutrons and protons each), which decay to stable
calcium and iron, respectively. The radioactive energy thus released
makes the supernova shine bright for many years.
Because of the wild boiling of the neutrino-heated gas, the blast
wave starts out non-spherically and imprints a large-scale asymmetry on
the ejected stellar matter and the supernova as a whole (Fig. 1), in
agreement with the observation of clumpiness and asymmetries in many
supernovae and their gaseous remnants. The initial asymmetry of the
explosion has two immediate consequences. On the one hand, the neutron
star receives a recoil momentum opposite to the direction of the
stronger explosion, where the supernova gas is expelled with more
violence. This effect is similar to the kick a rowing boat receives when
a passenger jumps off. On the other hand, the production of heavy
elements from silicon to iron, in particular also of titanium and
nickel, is more efficient in directions where the explosion is stronger
and where more matter is heated to high temperatures.
The physical processes that trigger and drive the explosion have been
an unsolved puzzle for more than 50 years. One of the theoretical
mechanisms proposed invokes the neutrinos, because they carry away more
than hundred times the energy needed for a typical supernova. As the
neutrinos leak out from the hot interior of the neutron star, a small
fraction of them is absorbed in the surrounding gas. This heating causes
violent motions of the gas, similar to those in a pot of boiling water.
When the bubbling of the gas becomes sufficiently powerful, the
supernova explosion sets in as if the lid of the pot was blown off. The
outer layers of the dying star are then expelled into circumstellar
space, and with them all the chemical elements that the star has
assembled by nuclear burning during its life. But also new elements are
created in the hot ejecta of the explosion, among them radioactive
species such as titanium (44Ti with 22 protons and 22 neutrons) and
nickel (56Ni with 28 neutrons and protons each), which decay to stable
calcium and iron, respectively. The radioactive energy thus released
makes the supernova shine bright for many years.
Because of the wild boiling of the neutrino-heated gas, the blast
wave starts out non-spherically and imprints a large-scale asymmetry on
the ejected stellar matter and the supernova as a whole (Fig. 1), in
agreement with the observation of clumpiness and asymmetries in many
supernovae and their gaseous remnants. The initial asymmetry of the
explosion has two immediate consequences. On the one hand, the neutron
star receives a recoil momentum opposite to the direction of the
stronger explosion, where the supernova gas is expelled with more
violence. This effect is similar to the kick a rowing boat receives when
a passenger jumps off. On the other hand, the production of heavy
elements from silicon to iron, in particular also of titanium and
nickel, is more efficient in directions where the explosion is stronger
and where more matter is heated to high temperatures.
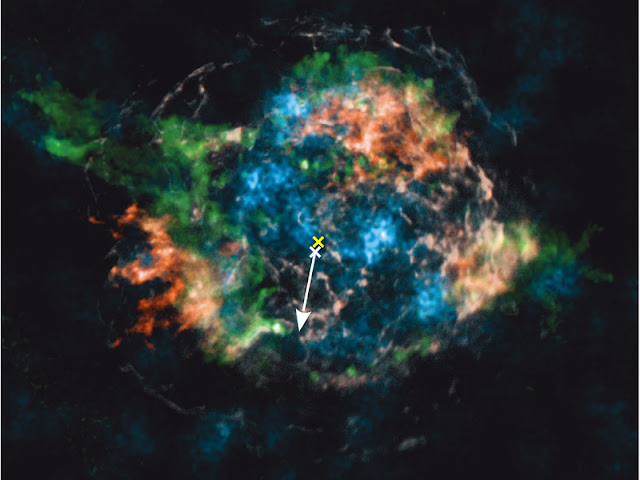
Fig. 2a: Observed distribution of radioactive titanium (44Ti, blue) and iron
(white, red) in Cassiopeia A. The visible iron is mostly the radioactive
decay product of radioactive nickel (56Ni). The yellow cross marks the
geometrical centre of the explosion, the white cross and the arrow
indicate the current location and the direction of motion of the neutron
star. Copyright:
Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Nature; from Grefenstette et al., Nature 506,
339 (2014); Fe distribution courtesy of U.~Hwang.
"We have predicted both effects some years ago by our
three-dimensional (3D) simulations of neutrino-driven supernova
explosions", says Annop Wongwathanarat, researcher at RIKEN and lead
author of the corresponding publication of 2013, when he worked at MPA
in collaboration with his co-authors H.-Thomas Janka and Ewald Müller.
"The asymmetry of the radioactive ejecta is more pronounced if the
neutron star kick is larger", he adds. Since the radioactive atomic
nuclei are synthesized in the innermost regions of the supernova, in
very close vicinity to the neutron star, their spatial distribution
reflects explosion asymmetries most directly.
New observations of Cassiopeia A (Cas A), the gaseous remnant of a
supernova whose light reached the Earth around the year 1680, could now
confirm this theoretical prediction. Because of its young age and
relative proximity at a distance of just 11,000 light years, Cas A
offers two great advantages for measurements. First, the radioactive
decay of 44Ti is still an efficient energy source and releases
high-energy X-ray radiation, therefore the presence of this atomic
nucleus can be mapped in 3D with high precision. Second, the velocity of
the neutron star is known with both its magnitude and its direction on
the plane of the sky. Since the neutron star propagates with an
estimated speed of at least 350 kilometres per second, the asymmetry in
the spatial distribution of the radioactive elements is expected to be
very pronounced. Exactly this is seen in the observations (Fig. 2a).
Fig. 2b: Observable radioactive nickel (56Ni, green) and titanium (44Ti, blue)
as predicted by the 3D simulation of a neutrino-driven supernova
explosion shown in Fig. 1. The orientation is optimized for closest
possible similarity to the Cas A image of Fig. 2a. The neutron star is
marked by a white cross and shifted away from the centre of the
explosion (red plus symbol) because of its kick velocity. The neutron
star motion points away from the hemisphere that contains most of the
ejected 44Ti. Iron (the decay product of Ni56) can be observed only in
an outer, hot shell of Cas A. © MPA
While the compact remnant speeds toward the lower hemisphere, the
biggest and brightest clumps with most of the 44Ti are found in the
upper half of the gas remnant. The computer simulation, viewed from a
suitably chosen direction, exhibits a striking similarity to the
observational image (Fig. 2b). This can also be seen when comparing the
3D visualisation of the simulations in Fig. 3 with the 3D imaging of Cas A.
But not only the spatial distributions of titanium and iron resemble those in Cas A. Also the total amounts of these elements, their expansion velocities, and the velocity of the neutron star are in amazing agreement with those of Cas A. "This ability to reproduce basic properties of the observations impressively confirms that Cas A may be the remnant of a neutrino-driven supernova with its violent gas motions around the nascent neutron star", concludes H.-Thomas Janka.
But more work is needed to finally prove that the explosions of massive stars are indeed powered by energy input from neutrinos. "Cas A is an object of so much interest and importance that we must also understand the spatial distributions of other chemical species such as silicon, argon, neon, and oxygen", remarks Ewald Müller, pointing to the beautiful multi-component morphology of Cas A revealed by 3D imaging. Just having one example is also not enough for making a fully convincing case. Therefore the team has joined a bigger collaboration to test the theoretical predictions for neutrino-driven explosions by a close analysis of a larger sample of young supernova remnants. Step by step the researchers thus hope to collect evidence to be able to settle the long-standing problem of the supernova mechanism.
HTJ
But not only the spatial distributions of titanium and iron resemble those in Cas A. Also the total amounts of these elements, their expansion velocities, and the velocity of the neutron star are in amazing agreement with those of Cas A. "This ability to reproduce basic properties of the observations impressively confirms that Cas A may be the remnant of a neutrino-driven supernova with its violent gas motions around the nascent neutron star", concludes H.-Thomas Janka.
But more work is needed to finally prove that the explosions of massive stars are indeed powered by energy input from neutrinos. "Cas A is an object of so much interest and importance that we must also understand the spatial distributions of other chemical species such as silicon, argon, neon, and oxygen", remarks Ewald Müller, pointing to the beautiful multi-component morphology of Cas A revealed by 3D imaging. Just having one example is also not enough for making a fully convincing case. Therefore the team has joined a bigger collaboration to test the theoretical predictions for neutrino-driven explosions by a close analysis of a larger sample of young supernova remnants. Step by step the researchers thus hope to collect evidence to be able to settle the long-standing problem of the supernova mechanism.
HTJ
June 21, 2017
Interactive 3D visualization of the spatial distribution of 56Ni ejected in the neutrino-driven supernova simulation of Fig. 1.
Contact
Phone:
2228
Email: thj@mpa-garching.mpg.de
Links:
personal homepage (the institute is not responsible for the contents of personal homepages)
Interactive 3D visualization of the spatial distribution of 56Ni ejected in the neutrino-driven supernova simulation of Fig. 1.
Abb. 3b: 44Ti
June 21, 2017
Interactive 3D visualization of the spatial distribution of 44Ti
ejected in the neutrino-driven supernova simulation of Fig. 1.
Acknowledgments:
This project was partly funded by the European Research Council through grant ERC-AdG No. 341157-COCO2CASA, by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft through Excellence Cluster "Universe" EXC-153, and by a RIKEN iTHES Project. The simulations and their post-processing were conducted on the IBM iDataPlex Systems draco and hydra of the Max Planck Computing and Data Facility (MPCDF).
Contact
Scientific Staff Phone: 2209
Email: emueller@mpa-garching.mpg.de
Links: personal homepage (the institute is not responsible for the contents of personal homepages)
Hämmerle, Hannelore
Press officer
Phone: 3980
Email: hanne@mpa-garching.mpg.de
Original Publication
1. Wongwathanarat, A.; Janka, H.-Th.; Mueller, E.; Pllumbi, E.; Wanajo, S.
Production and Distribution of 44Ti and 56Ni in a Three-dimensional Supernova Model Resembling Cassiopeia A
ApJ 842 13
More Information
MPG Press Release
Radioactive elements in Cassiopeia A suggest a neutrino-driven explosion
RIKEN Press Release