Radio telescopes observe the sky in a very indirect fashion. Sky images in the radio frequency range therefore have to be computed using sophisticated algorithms. Scientists at the MPI for Astrophysics have developed a series of improvements for these algorithms, which help to improve the telescopes' resolution considerably.
Optical telescopes produce data, which are a direct representation of the observed object's brightness distribution, i.e. an image in the conventional sense, which can be used for further analysis without additional processing. In radio interferometry (i.e. the high-resolution observation of the sky at radio frequencies), the situation is more complicated: here one does not obtain the sky brightness at a specific location, but rather data points indicating the amount, frequency and direction of brightness fluctuations.
If these data points were arranged on a regular two-dimensional grid, converting them to a normal image would be straightforward, but unfortunately no radio telescope design exists which could produce this arrangement. Realistic data point distributions often exhibit complex, inhomogeneous patterns (see fig. 3). Further complications arise if the individual antennae are not placed perfectly on a single plane, and/or if the observed sky region is too large to be approximated by a flat surface. In this case, additional correction terms have to be applied during the image generation, which further increases the computational cost.
The operation described above is called "gridding" and in practice various different implementations exist. Some are not particularly accurate (usually because they date back to the early times of radio astronomy, when computational power was very limited and many approximations and simplifications had to be made). Others provide good accuracy, but often are not fast enough to process the huge amounts of data produced by contemporary radio telescopes in an acceptable amount of time.
Scientists at MPA have now used various approaches – both from both radio astronomy itself and from unrelated scientific areas – to implement a new version of the gridding operation. This new implementation produces very accurate results while at the same time consuming considerably less CPU time and computer memory.
Gridding, however, is only one of several components necessary to produce realistic images from interferometric observations. To suppress noise in the data and eliminate the directional changes in antenna sensitivity, sophisticated iterative algorithms are employed. Traditionally, very often a variant of the so-called CLEAN algorithm is used, which is comparatively quick but does not provide an uncertainty estimate for the resulting image. In contrast to CLEAN-based methods, the MPA scientists developed an (admittedly significantly slower) approach, which delivers physically motivated results including error bars, making use of Information Field Theory and Bayesian statistics.
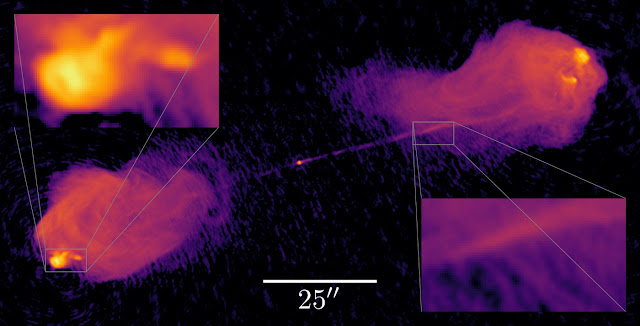
Fig. 4 shows a comparison of the two methods. The observed astrophysical source is the radio galaxy Cygnus A with a supermassive black hole (weighing more than a billion solar masses) at its centre. Two jets, observable at radio wavelengths, leave this centre and at some point encounter the intergalactic medium, where they are reflected and start to emit very brightly. The back-flows create large volumes of radio-bright gas, which can be observed with radio interferometers like the VLA.
The image obtained with the new algorithm exhibits significantly better spatial resolution in the bright image regions, since the signal-to-noise ratio in these areas is much higher. At the same time, it does not show the pronounced structures in the darker regions from the CLEAN results; presumably these structures are artefacts of the CLEAN algorithm which do not correspond to real features on the sky.
The methods presented here essentially open up two new possibilities
for radio astronomy: they allow re-processing of already existing data
sets, in order to gain additional insights from the improved images. For
future observations, there may now be an option to reach the desired
image quality with shorter observation times, thanks to the improvements
in the algorithms, allowing for a higher overall number of
observations. Source: Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics
Other scientific disciplines such as medical imaging, especially magneto-resonance tomography (MRT) employ imaging techniques that are closely related to those in radio interferometry. It is therefore possible that the insights gained from these developments will be beneficial in these areas as well.
Additional information:
The two last images from Fig 4 can be enlarged separately below.
© MPA; reconstruction: NRAO, Klasse Richard A. Perley
© MPA
Authors
Arras, Philipp Arras
PhD student
Tel: 2034
Martin Reinecke
Scientific Staff
Enßlin, Torsten Enßlin
Scientific Staff
Tel.:2243
Original publications
1. P. Arras, R.A. Perley, H.L. Bester, R. Leike, O. Smirnov, R. Westermann, T.A. Enßlin Comparison of classical and Bayesian imaging in radio interferometry. Cygnus A with CLEAN and resolve A&A, Forthcoming article
Source/ DOI
Efficient wide-field radio interferometry response A&A, accepted
3.Ye, H.
Accurate image reconstruction in radio interferometry
Doctoral thesis
Source/DOI
4. Alex H. Barnett, Jeremy F. Magland, Ludvig af Klinteberg A parallel non-uniform fast Fourier transform library based on an "exponential of semicircle" kernel SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 41, 5, C479--C504, 2019